Sealing & Calculation of Sealing Force of Titanium Alloy Metal Seated Ball Valves
The sphere and valve seat of the ball valve are generally made from titanium alloy due to process characteristics of the PTA device such as high temperature, high pressure and corrosion, and a metal hard seal is adopted. In order to avoid the occurrence of stucking of the metal, it is required that there should be a certain hardness difference between the metal sliding contact surface of the ball and the valve seat. In actual production and operation, the hardness difference between the ball and the valve seat is generally between 5 and 10HRC to ensure that the ball valve has a long service life. Compared with the valve seat, the processing technology of the sphere is more complicated, and the processing cost is relatively high. Therefore, from the perspective of economy, the surface hardness of the sphere should be higher than that of the valve seat.
Ensuring that the friction between the titanium alloy hard-sealed ball valve and the sealing pair of the valve seat does not cause wear or scratches in the opening and closing process of the ball is the key to studying this kind of valve. The surface hardness and wear resistance of titanium alloy balls and valve seat sealing surfaces are usually improved by surface hardening treatment. Different from steel parts, the surface treatment of titanium alloy parts is relatively simple, and the surface hardened layer is required to have the characteristics of corrosion resistance, high-temperature resistance and wear resistance. At present, the main process technology used in China is the composite process of nitriding plus TiN, but the current process is relatively unstable, and falling and scratches are prone to happen for the hardened layer during the opening and closing of the ball valve. In order to ensure that the hardened layer is not damaged in the opening and closing process of the ball valve and ensure a good seal, it is necessary to calculate and analyze the specific pressure of the seal to obtain the minimum specific pressure for effective sealing. The sealing structure of the titanium alloy hard-sealed ball valve of a size of 10 inches and pressure 300Lb is analyzed as an example, and the specific pressure of the sealing is calculated in this article.
1. The design of the sealing structure
A trunnion ball is adopted for titanium alloy hard sealing ball valves with a size of 10 inches and pressure 300Lb. The valve seat and the sphere are made from titanium alloy, and the sealing pair adopts the surface hardening treatment to improve its wear resistance and surface hardness. The sealing structure is mainly composed of balls, valve seats, O rings, graphite sealing rings and disc springs, and the structure is shown in Figure 1. The sealing surface of the valve seat is designed with a scraper structure, and the impurities or particles on the surface of the sphere can be scraped during the rotation of the sphere. Low-pressure sealing of the ball valve seat is achieved by the pre-tightening force provided by the dis spring. When the medium flows, under the combined action of the medium pressure and the pre-tightening force of the disc spring, the valve seat is pushed toward the ball to achieve reliable sealing between the ball and the valve seat.
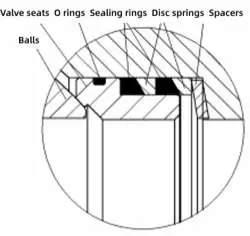
Figure 1 The schematic diagram of the sealing structure
2. Calculation of sealing force
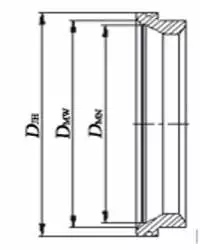
Figure 2 The schematic diagram of the structure and dimensions of valve seats
The sealing force Q and the force Q0 generated by the fluid pressure on the sealing surface of the valve seat are calculated according to the following formula:
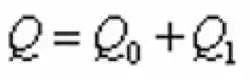 (1)
(1)
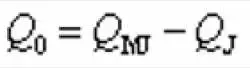 (2)
(2)
In the formula, Q is the sealing force of the trunnion ball valve. Q0 is the force generated by the fluid pressure on the sealing surface of the valve seat. Q1 is the disc spring pretightening force. QMJ is the force of hydrostatic pressure on the seat sealing surface. QJ is the force of hydrostatic pressure in the clearance of the valve seat’s sealing surface.
The formula for calculating the force QMJ of the hydrostatic pressure on the sealing surface of the valve seat is as follows:
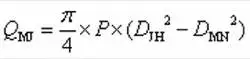 (3)
(3)
The formula for calculating the force QJ of the hydrostatic pressure in the clearance of the valve seat sealing surface is as follows:
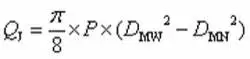 (4)
(4)
The calculation formula of pretightening force of the disc spring Q1 is as follows:
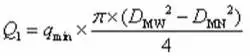 (5)
(5)
The calculation of the sealing specific pressure is calculated according to the following formula:
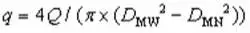 (6)
(6)
In the formula, q is the calculated specific pressure of the sealing surface. Qmin is minimum preload specific pressure. P is the design pressure. DMW is the outer diameter of the seat’s sealing surface. DMN is the inner diameter of the seat’s sealing surface. DJH is the outer diameter of the seat seal piston.
According to the design manual, the calculated specific pressure of the sealing surface of the ball valve should meet the following conditions:
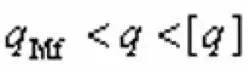 (7)
(7)
In the formula, q is the allowable specific pressure of the sealing surface. See Table 1 for the values. qMF is the necessary specific pressure of the sealing surface.
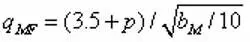 (8)
(8)
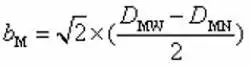 (9)
(9)
Table 1 The allowable specific pressure of the sealing surface
Ensuring that the friction between the titanium alloy hard-sealed ball valve and the sealing pair of the valve seat does not cause wear or scratches in the opening and closing process of the ball is the key to studying this kind of valve. The surface hardness and wear resistance of titanium alloy balls and valve seat sealing surfaces are usually improved by surface hardening treatment. Different from steel parts, the surface treatment of titanium alloy parts is relatively simple, and the surface hardened layer is required to have the characteristics of corrosion resistance, high-temperature resistance and wear resistance. At present, the main process technology used in China is the composite process of nitriding plus TiN, but the current process is relatively unstable, and falling and scratches are prone to happen for the hardened layer during the opening and closing of the ball valve. In order to ensure that the hardened layer is not damaged in the opening and closing process of the ball valve and ensure a good seal, it is necessary to calculate and analyze the specific pressure of the seal to obtain the minimum specific pressure for effective sealing. The sealing structure of the titanium alloy hard-sealed ball valve of a size of 10 inches and pressure 300Lb is analyzed as an example, and the specific pressure of the sealing is calculated in this article.
1. The design of the sealing structure
A trunnion ball is adopted for titanium alloy hard sealing ball valves with a size of 10 inches and pressure 300Lb. The valve seat and the sphere are made from titanium alloy, and the sealing pair adopts the surface hardening treatment to improve its wear resistance and surface hardness. The sealing structure is mainly composed of balls, valve seats, O rings, graphite sealing rings and disc springs, and the structure is shown in Figure 1. The sealing surface of the valve seat is designed with a scraper structure, and the impurities or particles on the surface of the sphere can be scraped during the rotation of the sphere. Low-pressure sealing of the ball valve seat is achieved by the pre-tightening force provided by the dis spring. When the medium flows, under the combined action of the medium pressure and the pre-tightening force of the disc spring, the valve seat is pushed toward the ball to achieve reliable sealing between the ball and the valve seat.

Figure 1 The schematic diagram of the sealing structure
2. Calculation of sealing force

Figure 2 The schematic diagram of the structure and dimensions of valve seats
The sealing force Q and the force Q0 generated by the fluid pressure on the sealing surface of the valve seat are calculated according to the following formula:
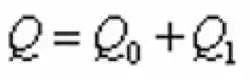 (1)
(1)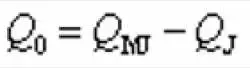 (2)
(2)In the formula, Q is the sealing force of the trunnion ball valve. Q0 is the force generated by the fluid pressure on the sealing surface of the valve seat. Q1 is the disc spring pretightening force. QMJ is the force of hydrostatic pressure on the seat sealing surface. QJ is the force of hydrostatic pressure in the clearance of the valve seat’s sealing surface.
The formula for calculating the force QMJ of the hydrostatic pressure on the sealing surface of the valve seat is as follows:
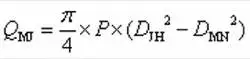 (3)
(3)The formula for calculating the force QJ of the hydrostatic pressure in the clearance of the valve seat sealing surface is as follows:
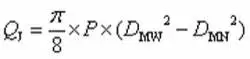 (4)
(4)The calculation formula of pretightening force of the disc spring Q1 is as follows:
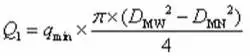 (5)
(5)The calculation of the sealing specific pressure is calculated according to the following formula:
In the formula, q is the calculated specific pressure of the sealing surface. Qmin is minimum preload specific pressure. P is the design pressure. DMW is the outer diameter of the seat’s sealing surface. DMN is the inner diameter of the seat’s sealing surface. DJH is the outer diameter of the seat seal piston.
According to the design manual, the calculated specific pressure of the sealing surface of the ball valve should meet the following conditions:
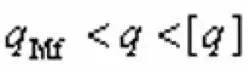 (7)
(7)In the formula, q is the allowable specific pressure of the sealing surface. See Table 1 for the values. qMF is the necessary specific pressure of the sealing surface.
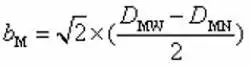 (9)
(9)Table 1 The allowable specific pressure of the sealing surface
| Materials | Manufacturing | Hardness | Allowable specific pressure/MPa | |
| No sliding friction on the sealing surface | Sliding friction on the sealing surface | |||
| Carbon steel | Casting | 170HBS | 100 | 30 |
| Nitrided steel |
Nitridation and casting | 800 to 1000HV | 300 | 80 |
| Stainless actinium | Calendering and surfacing |
200 to 300HBS | 250 | 45 |
| Acid resistant steel | Casting and Calendering | 140 to 170HBS | 150 | 40 |
| Cobalt based hard alloy | Surfacing | 48 to 51HRC | 150 | 50 |
| Surfacing | 40 to 45HRC | 250 | 80 | |
There is no relevant test value for the allowable specific pressure of titanium alloy in the design manual. The hardness of the hardened layer of the valve seat of the titanium alloy hard sealing ball valve studied in this article can reach 1000HV. Therefore, the allowable specific pressure refers to the value of nitrided steel, and the relevant design data of the titanium alloy hard-sealed trunnion ball valve with a size of 10 inches and pressure 300Lb is calculated by the above formula; the calculated specific pressure of the sealing surface is 22MPa, which meets the requirements of formula (7).



