Localization Transformation of Pipe Filters in Pumping Stations
Abstract
This paper provides an overview of the localization of the retrofit process for pipeline filters in the centralized pumping stations of the Tonggang Steelmaking Division. It first addresses the challenges related to the supply of spare parts encountered during filter maintenance, then discusses how the localization of the retrofit process reduces spare parts costs, and finally highlights the enhancement of maintenance personnel's technical expertise through these upgrades. By comparing the key parameters of imported and domestic filters—such as filtration accuracy, pressure, flow rate, and filter cartridge materials—and analyzing performance data from post-installation tests, the results demonstrate that domestic filters can fully replace imported ones. Replacing only critical components, such as filter cartridges and sealing elements, achieves the localization of spare parts, resulting in a significant reduction in spare parts costs.
1. Introduction
In recent years, large domestic steel enterprises have increasingly upgraded their energy-saving and emission-reduction technologies, placing greater demands on industrial wastewater separation equipment. To support these efforts, the Tonggang Steelmaking Division selected pipeline filters imported from Israel for the design of the water system in its centralized pumping stations. Since the commissioning of the pumping stations in 2014, the filters have operated normally; however, the imported equipment lacked spare parts and technical documentation.
After prolonged operation, the sealing elements began leaking, and nozzle blockages occurred in the water system, impacting product quality. Due to the absence of technical documentation for the imported equipment, the specifications and design details of the sealing elements and filter cartridges were unclear. As a result, replacement parts could not be procured for an extended period, and the cost of imported components was exceptionally high, with each filter cartridge priced at 200,000 RMB. To address the challenges related to spare parts and maintenance, the filters were disassembled during scheduled maintenance. Reputable domestic filter manufacturers were engaged to reverse engineer critical components, such as sealing elements and filter cartridges. This localization retrofit effectively resolved the maintenance issues and improved equipment reliability.
2. Reasons for Improvement
The pipeline filters in the Steelmaking Division's centralized pumping station water system were imported from Israel, posing challenges in sourcing common replacement parts, such as seals and filter cartridges. When the system was first installed and commissioned, the filters operated efficiently with few issues. However, over time, the filters developed leaks and blocked nozzles, and some components reached the end of their operational service life, resulting in frequent failures. Replacing the damaged parts was essential to restore optimal equipment performance and maintain uninterrupted production. Despite the procurement department's ongoing efforts, suppliers were unwilling to supply the necessary spare parts, and the issue remained unresolved until the end of 2021. The primary challenge was the prohibitively high cost of imported spare parts, coupled with the significant risks faced by suppliers. If the spare parts had dimensional inconsistencies or other quality issues, managing them would be difficult.
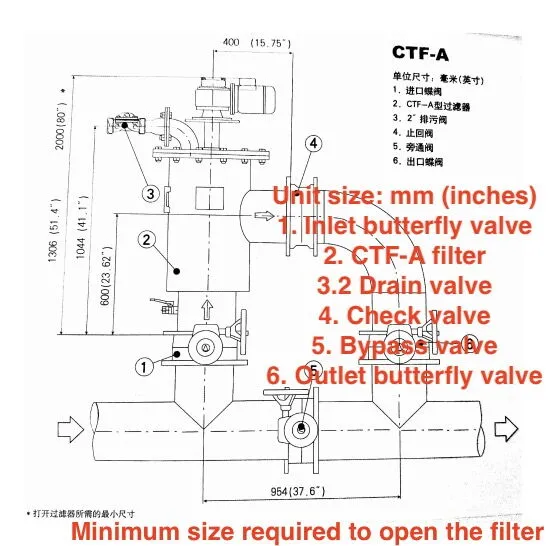
Figure 1: Working Principle
2.1 Condition Before Improvement
In the open-circuit water system, water passes through the filter cartridge, with pressure sensors installed on both the inlet and outlet pipes to measure the pressure differential. As the filter operates, the pressure differential rises. When it reaches the preset value of 0.2 MPa, the automatic cleaning cycle is triggered. During this process, the wire brush inside the filter rotates to remove debris from the filter cartridge and flush it out through backwashing. The cleaning cycle lasts 15–20 seconds. The filter cartridge is constructed from 316L stainless steel.
Figure 1 illustrates the working principle. Water flows into the filter via pipeline 1, and the filtered clean water passes through valves 4 and 6 before flowing through the main pipeline into the production water system, supplying purified water for production. Initially, the system operates smoothly with few issues. However, over time, continuous operation causes parts to age, leading to issues such as leaks and nozzle blockages. When the filter fails, repairs are difficult due to the unavailability of spare parts. Furthermore, the water system supplies production water to both the converter and billet production lines. Due to short shutdown periods, there is insufficient time for filter disassembly and repair during production. The unavailability of spare parts leads to the continued operation of the water system filter with unresolved issues.
2.2 Analysis of Common Faults and Causes
• Filter Leakage
Cause: The filter seals, including the rotating seal on the stainless steel brush, upper and lower lip seals of the filter cartridge, and static O-ring, are worn or damaged. Due to unclear specifications for the sealing elements, leakage is temporarily addressed with packing seals or sealants during short shutdowns. However, the root cause remains unresolved due to the unavailability of spare parts.
• Drainage Failure
Cause: The drain valve diaphragm is damaged, the pilot control valve core is stuck, and the electromagnet is faulty. Since the drain valve is an imported part, a domestic rubber manufacturer was contracted to produce the diaphragm. However, the domestic diaphragm fails to meet performance requirements and typically fails within a week of use. As a result, the entire drain valve must be replaced. Efforts to identify alternative domestic diaphragm suppliers are still in progress.
• Poor Water Quality Blocking the Nozzle
Cause: Damage to the upper and lower seals of the filter cartridge allows dirt to enter the system. Similarly, damage to the filter cartridge itself allows dirt to enter the system. After filter failure, the bypass is activated to maintain production, allowing dirt to enter the water system directly.
3. Improvement Measures
• Evaluate the feasibility of replacing imported filter components with domestic alternatives. Collaborate with the procurement department and qualified manufacturers to explore localization opportunities. The filter manufacturer compared its products to the existing filters, evaluating parameters such as filtration accuracy, construction, and cleaning methods. Our filters are rated at 100μm and 200μm, while the domestic filters range from 30μm to 3000μm, with customizable options to meet site-specific needs. In terms of construction, our filters use stainless steel, while theirs include woven filters with PVC support, sintered mesh with an all-stainless steel structure, and wedge mesh, all of which can be customized to meet specific requirements. Cleaning methods were also compared: our imported filters feature automatic cleaning activated by preset pressure differentials or time intervals, with the stainless steel brush rotating to remove impurities and discharge them through the drain valve within 15 to 20 seconds. Domestic filters employ a similar cleaning process. The analysis confirmed that domestic filters can fully replace the imported ones, meeting all required material specifications.
• Before purchasing new filter components, temporarily seal the sealing elements and filter cartridges with available materials to address leaks. The original filter cartridges will be retained for future measurement and mapping.
• Standardize operations by switching to manual cleaning when automatic cleaning is ineffective. Set the automatic cleaning interval to 2 hours, monitor cleaning effectiveness and pressure differentials each shift, and initiate manual cleaning when necessary.
• Source domestic replacements for commonly damaged diaphragms, such as those in drain valves. The drain valve, an imported component priced at approximately 5,000 RMB for 3-inch valves, requires replacement at least once a year. The diaphragm is the most frequently damaged component. Sourcing a domestic diaphragm could reduce spare parts costs by approximately 20,000 RMB annually.
4. Improvement Plan and Solution
Improvement Plan: Localization of Sealing Elements and Filter Cartridges
• Investigate the localization of sealing elements and filter cartridges that have reached the end of their service life. The manufacturer's filtration design is largely similar to the imported filters from Israel. The sealing components and filter cartridges should be disassembled and documented.
Solution:
① Manufacture filter cartridges to meet required filtration accuracy based on measured dimensions (material: 316L). The required filtration accuracy is primarily 100μm and 200μm, and the structure will follow the specifications of the imported parts.
② Disassemble the sealing element, inspect its configuration, and produce replacements tailored to site conditions (material: fluororubber). The design will follow the mold of the imported parts.
③ Reuse the filter body and automatic control device without modification. Only the filter cartridges and sealing elements need to be replaced for localization, resulting in significant cost savings on spare parts.
Improvement Plan: Surveying and Mapping for Localization
• Notify the equipment management department about the localization project for filter components and coordinate with domestic manufacturers to schedule surveying and mapping during maintenance. The steel line maintenance plan for November 2021 has been finalized. One week before the production shutdown, the filter manufacturer will be informed to utilize the maintenance window for surveying the filter cartridges and seals.
• The centralized pumping station water system serves both the converter production line and billet production line. Based on the production and maintenance schedules, the domestic filter manufacturer will be notified in advance. The 4# billet equipment is scheduled for repair from November 3, 2021, for 7 days. The manufacturer’s technicians will arrive at Tonggang before November 3 to prepare necessary surveying tools.
• The operations team will prepare for filter dismantling and begin the process on November 3, 2021, ensuring the protection of on-site components and facilitating the manufacturer's mapping process.
Improvement Plan: Localization and Replacement of Imported Filters and Domestic Spare Parts
• The purchasing department signed the supply contract on schedule, and the manufacturer produced and delivered the domestic modification parts on time. After mapping the closed-circuit filter components, the manufacturer produced and delivered the parts, which arrived on January 12, 2022.
• The operations team organized the installation and commissioning of the equipment according to the scheduled maintenance plan and tracked the domestic filters. After the domestic spare parts for the closed-circuit filter arrived, the operations team used the scheduled maintenance window to implement the domestic modification, and the system went online on January 21, 2022.
• After 3 months of testing, if the system meets production and operational requirements, the manufacturer will produce additional mapped filter components.
• If the system does not meet production and operational requirements, continue exploring other reputable domestic filter manufacturers for further localization.
In January 2022, we began domestic improvements to the filter cartridges, stainless steel brushes, and sealing elements of the closed-circuit water system filters at the centralized pump station. After three months of observation, the improvements were successful and fully met the design specifications. Following this success, the equipment management team instructed the procurement department to proceed with the domestic transformation of the remaining five sets of imported filters at the centralized pump station, including the 4# continuous casting machine open circuit, crystallization, secondary cooling, and water system filters for the converter (e.g., oxygen gun, converter vaporization, etc.).
As a result of the transformation, challenges in sourcing imported filter parts and replacing spare parts during maintenance were resolved. Maintenance and repair costs were significantly reduced, and detailed information about the internal components of the imported filters was obtained, which provided valuable technical support for future maintenance. As shown in the table above, the annual consumption of spare parts was 1.2 million RMB for imported parts and 85,000 RMB for domestic parts, resulting in annual savings of 1.115 million RMB in spare parts costs.
5. Conclusion
Following the successful implementation of filter improvements in the closed-circuit water system for the 4# billet at the centralized pump station, the filters were individually inspected and upgraded during subsequent maintenance. This resolved challenges in sourcing imported parts, reduced maintenance costs, and ensured the safe and stable operation of both the converter and billet production lines.
The localization transformation significantly reduced equipment maintenance costs, enhanced technicians' maintenance capabilities, shortened the spare parts procurement cycle, and improved the operational reliability of the equipment. These improvements effectively addressed the challenges of procuring and repairing spare parts for imported equipment, providing strong support for the company's continuous and stable production.



